Περίληψη:
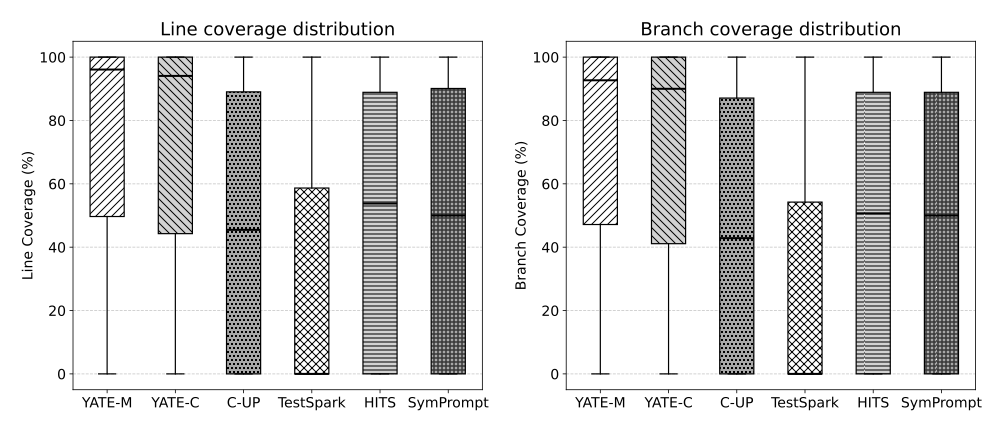
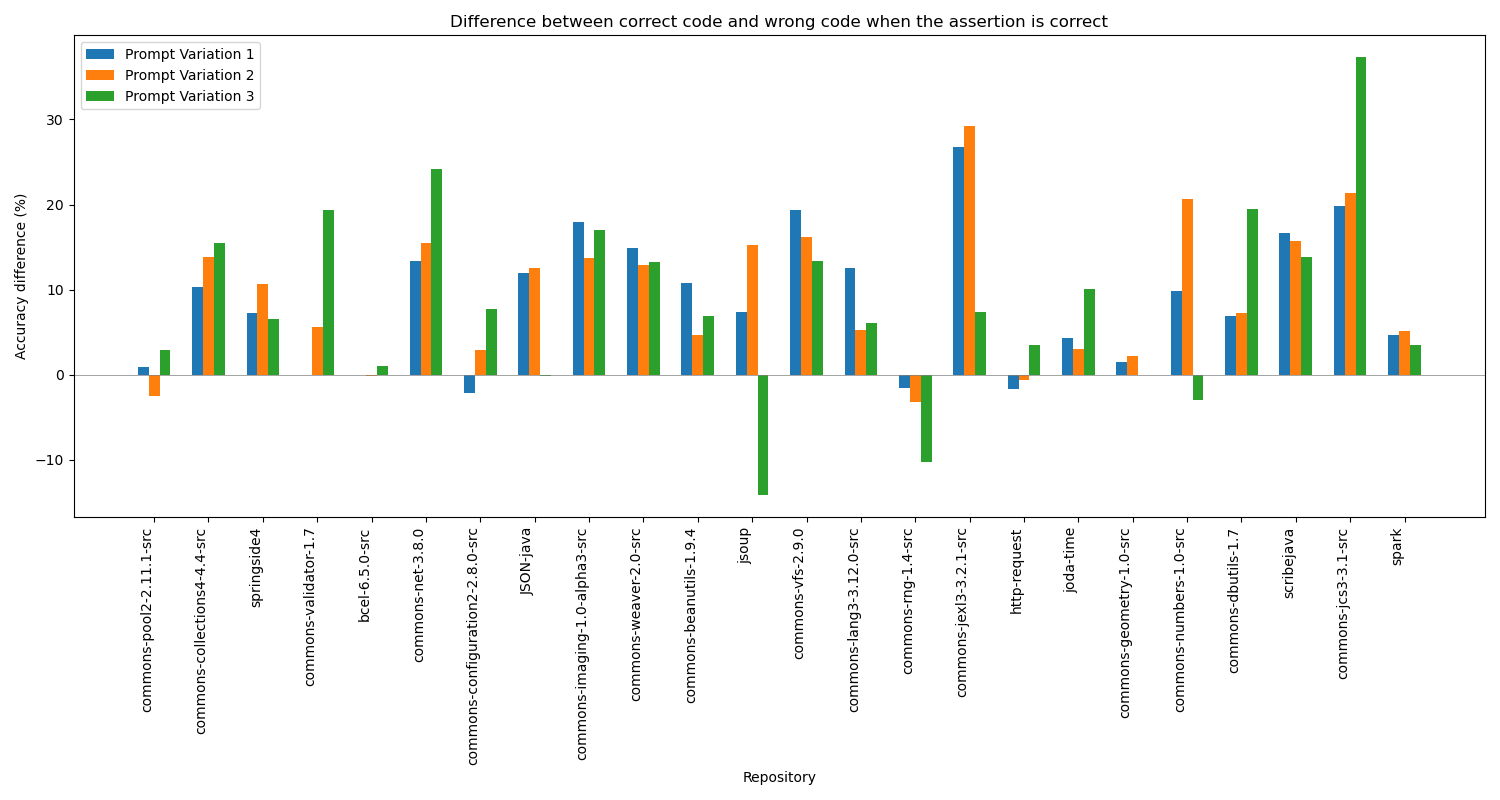
Recent advances in automated test generation utilises language models to produce unit tests. While effective, language models tend to generate many incorrect tests with respect to both syntax and semantics. Although such incorrect tests can be easily detected and discarded, they constitute a "missed opportunity" -- if fixed, they are often valuable as they directly add testing value (they effectively target the underlying program logic to be tested) and indirectly form good seeds for generating additional tests. To this end, we propose a simple technique for repairing some of these incorrect tests through a combination of rule-based static analysis and re-prompting. We evaluate this simple approach, named YATE, on a set of 6 open-source projects and show that it can effectively produce tests that cover on average 32.06% more lines and kill 21.77% more mutants than a plain LLM-based method. We also compare YATE with four other LLM-based methods, namely HITS, SYMPROMPT, TESTSPARK and COVERUP and show that it produces tests that cover substantially more code. YATE achieves 22% higher line coverage, 20% higher branch coverage and kill 20% more mutants at a comparable cost (number of calls to LLMs).
Διαβάστε περισσότερα : Σύνδεσμος